WHAT IS "TEXTILE"?
A textile is a flexible material made by creating an interlocking network of yarns or threads, which are produced by spinning raw fibers (either from natural or synthetic sources) into long and twisted lengths. Textiles are then formed by weaving, knitting, crocheting, knotting, tatting, felting, bonding braiding these yarns together.
Such as, a fabric is a material made through weaving, knitting, spreading, felting, stitching, crocheting or bonding that may be used in production of further products, for instance, clothing and upholstery.
THE WORD "TEXTILE"
The word 'textile' comes from the Latin adjective Textilis, meaning 'woven', which itself stems from Textus, the past participle of the verb Texere, 'to weave'.
The word 'fabric' also derives from Latin, with roots in the Proto-Indo-Eurepean language. Stemming most recently from the Middle French fabrique, or 'building', thing made', and earlier from the Latin fabrica ('workshop; an art, trade; a skillful production, structure, fabric'), the noun fabrica stems from the latin faber, or 'artisan who works in hard materials', which itself is derived from the Proto-Indo-European dhabh-, meaning 'to fit together'.
The word 'cloth' derives from the Old English clao, meaning a 'cloth, woven or felted material to wrap one', from the Proto-Germanic kalithaz, similar to the Old Frisian klath, the Middle Dutch cleet, the Middle High German kleit and German kleid, all meaning 'garment'.
CLASSIFICATION OF TEXTILES

Textiles refer to materials that are made from fibers, thin threads or filaments which are natural or manufactured or a combination. Thus according to the source of the ingredient of textile, we can classify it into three main categories:
1. Natural textiles
2. Man-made textiles and
3. Its' combination
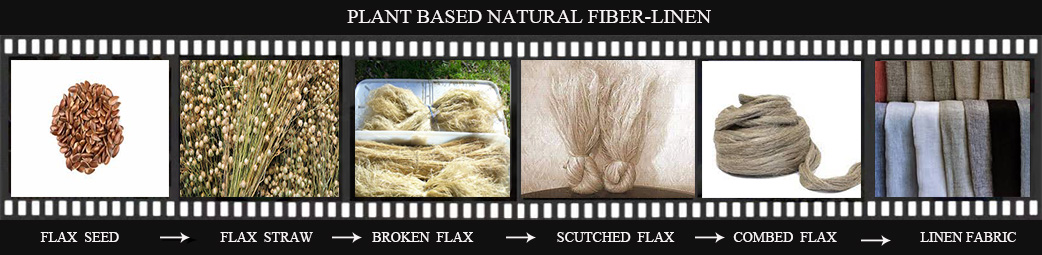
1. Natural textiles could be from either plant or animal. Such as wool, silk, skin, hair, fur etc are animal based fibers; cotton, linen, jute, hemp, sisal, bamboo, etc are from plants.
2. Man-made textiles are also called synthetic textiles. Such as polyester, nylon, acrylic, spandex, lurex, carbon fiber etc are called man-made textiles.
3. Combination or blended fiber: Fabric or yarn produced with a combination of two or more types of different fibers, or yarns to obtain desired traits. Blending is possible at various states of textile manufacturing. Natural and synthetic fibers can be blended such as polyester with cotton (TC/CVC etc).

According to the construction method of textiles, we can classify it into
core following groups:
- Knitted fabric
- Woven fabric and
- Non-woven fabric

1. Knitted fabric:
Knitted fabric is a textile that results from knitting, the process of inter-looping of yarns or inter-meshing of loops. Its properties are distinct from woven fabric in that it is more flexible and can more readily constructed into smaller pieces.
There are two basic varieties of knit fabric: weft-knit and warp-knit fabric. Warp-knitted fabrics such as tricot and milanese are resistant to runs and relatively easy to sew. This fabrics are commonly used in lingerie, functional wear, activewear and so on.
Weft-knit fabrics are easier to make and more common. When cut, they will unravel (run) unless repaired.
Knitted fabric are the most popular with single jersey, double jersey, french terry, ponte-de-roma, scuba, air-layer, waffle, fleece, sherpa, jacquard, tricot, net, lace and braid are in knitting fabric family.
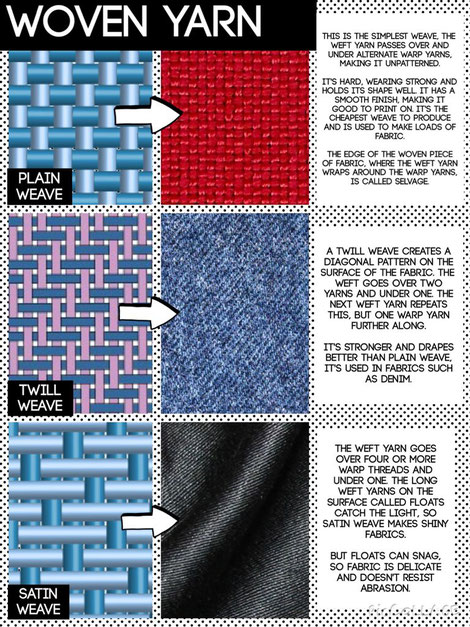
2. Woven fabric:
Woven fabric is any textile formed by weaving. Woven fabrics are often created on a loom, and made of many threads woven on a warp and a weft. Technically, a woven fabric is any fabric made by interlacing two or more threads at right angles to one another.
As per the weaving methods, woven fabrics can be classified into Plain Weave, Twill Weave and Satin Weave. We can also name "fancy weave"- an other types of woven fabrics including pile, jacquard, dobby and gauze.
Some popular woven fabric names are: Chiffon, Crepe, Denim, Linen, Satin and Silk.

3. Non-woven fabric:
Non-woven fabrics are gaining popularity in medical and home textile industry due to it's environment friendly properties.
As opposed to traditional materials, such as cotton, linen, wool and silk; non woven fabrics do not necessitate weaving or knitting felt one of the most common examples of non woven fabric. It's made by agitating fibers in a solution until they interlock into a dense textile.
Non-woven textiles tend to be weaker, easily torn fabrics, as the fibers are not held together in any structured, secure way.